Category: ancestors
Monacan Bulldozer

There’s lots of things that we can do with engineering, with big machines and modern equipment. I mean, there are lots of things that one could do.
And so we do have the ability to build up the soil and help create an island, an elevation that will then put a structure that is out of the 100 year floodplain. That’s true.
We also could pipe the creek and pave it over and then we wouldn’t have to have a buffer. You could actually get a permit from the Army Corps of Engineers to do things like that.
But should we?
That’s where I’m coming from. The 100 year floodplain has a very important hydrologic function in allowing, during a storm, as a water is rushing down, because it has this area it spreads out and dissipates the energy of the water and then some of that sediment load actually drops out in that slower water at the margins. That’s why floodplain soils are so rich, that’s why people like to farm them, because it’s some of the best soil, because that’s where those floodwaters dissipate and lose their energy.
When you constrict the area that the water is flowing through it goes faster. So on a large scale, looking at the whole area, I understand what Mr. Pohl is saying and I understand what Timmons has said, that this will not raise the elevation of the flood overall.
But I’m also looking at this from two perspectives; one is death by 1000 paper cuts, which is all the little fills cumulatively altogether, I don’t have the confidence that we’re looking at it from that perspective.
The other aspect is, again, what I just said about floodplains. They have a purpose and we really should not build in the floodplains. Albemarle County is actually more restrictive; we don’t let you put subdivisions in the floodplains.
You know, our neighbors in Charlottesville allowed a development of housing in the floodplain through an area which I used to kayak when the water was up.
And too bad for those folks when we get another big storm.
I believe very strongly and I have a 35 year career in floodplain and watershed management, and so I’ve spent my whole life trying to keep people out of floodplains.
I would also suggest to you that the zoning, yes is from 1997. But in our comp plan, never mind the park thing for a moment to my commissioner at the other end of the dais, they’re not suggesting this become a park necessarily, but it’s designated as green system because the county did go along and say all of these floodplains, we’re going to call them green systems.
Don’t always think of the Earth as just a place where we are going to recreate or not recreate. There are other ecological functions that are going on there for biota, for salamanders, for all kinds of other critters that are also under our stewardship.
Where I’m coming from is I’m not in favor of allowing fill in the floodplain.
I think that zoning can be old, zoning can be wrong. Zoning can be a bad idea. I think this zoning is outdated. I agree with Lonnie. There are a lot of a lot of reasons why we developed along rivers, that was because that was a transportation system. We had to move goods on the Rivanna. We put goods on batteaux on the Rivanna and sent them down to Richmond. So you know, there’s a lot of reasons why people develop near rivers, also for water supply.
But today, putting industrial along our rivers is also a bad idea. So I don’t think the zoning is good. We’re not here tonight to decide about the zoning, we are here to decide whether you think it’s OK to fill in the floodplain. And I’m going to stick with the comprehensive plan. I think it was wise to say that this is a green system and I don’t care if no one ever recreates in it. So that’s where I’m coming.
I have a lot of hydrologic reasons and ecological reasons for the way that I am presenting my position tonight. I don’t think we’re getting a huge return for allowing this site to become this industrial use by getting it out of the floodplain. That’s it.
I will now step down off my soapbox and yield to my colleagues.–Karen Firehock April 22, 2025 Albemarle County Planning Commission
Vikings

1200 years later the Vikings have good publicists. They connected Ireland to England and Europe. The slave taking and sword-work aren’t so much at the forefront of the narrative. They introduced us to trousers. OK. And the helmets…
Viking society only developed in the 9th century C.E., and there is no sign that Vikings really wore horned helmets. According to History.com, the legend likely originated with Scandinavian artists in the 1800s, who popularized portrayals of the nomadic raiders wearing the equipment in their works.
Emma Gray

Tripod
James Madison trending

James Madison.
The Project Gutenberg EBook of Browere’s Life Masks of Great Americans, by
Charles Henry Hart
the Quick and the Dead

into the light

Castanea dentata
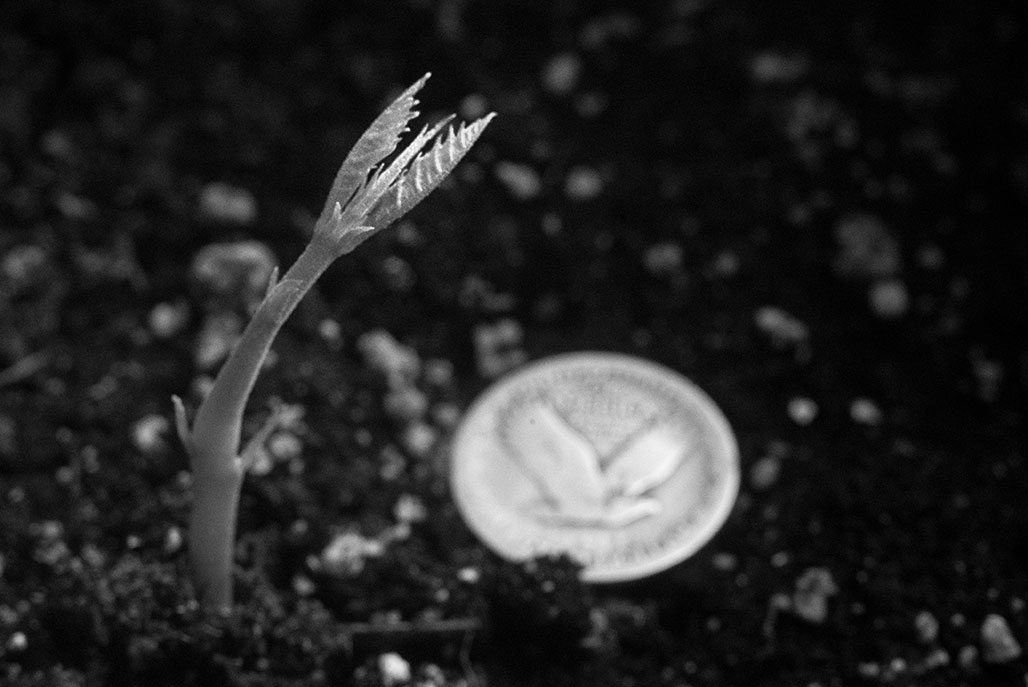
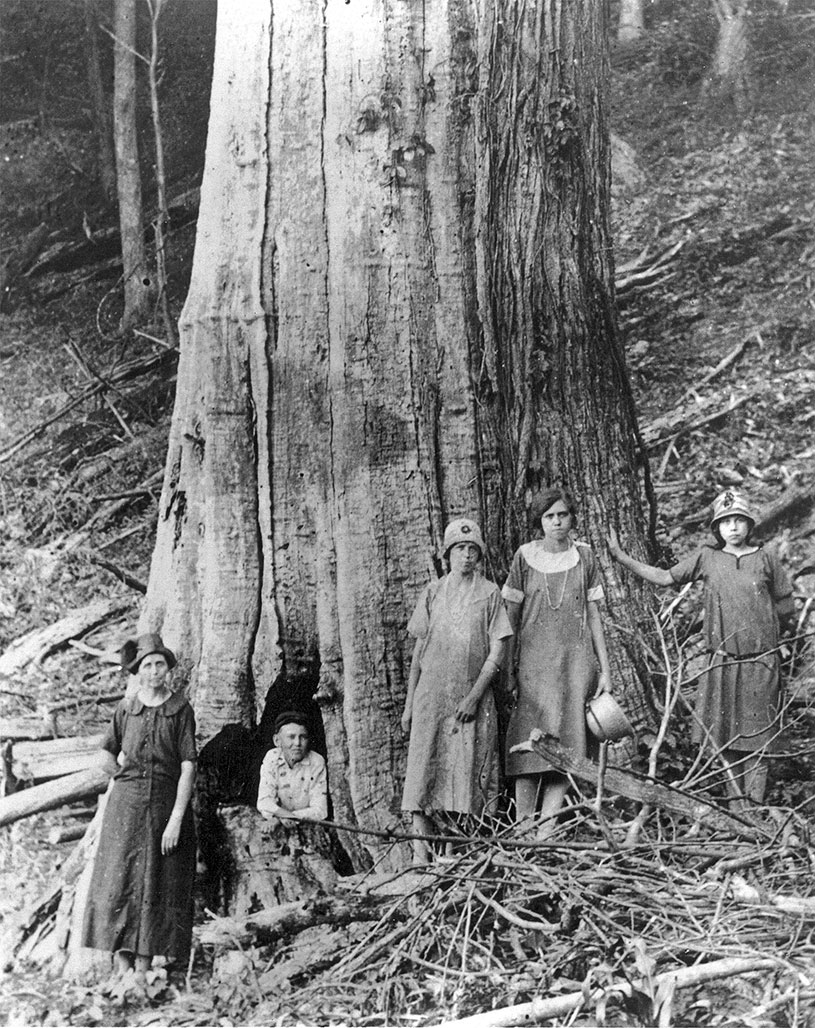


Greatest forest loss in history
The American chestnut is an historic and beloved part of America’s landscape. Its extinction would be the loss of a symbol of American strength, endurance and resourcefulness. Saving the chestnut and restoring it to its native range at scale could also help give other endangered tree species a new lease on life and directly offset the effects of climate change and deforestation. While no single intervention can completely eradicate chestnut blight, together the science of breeding, biotechnology, and biocontrol (3BUR) offer our best hope for rescuing the American chestnut tree.—The American Chestnut Foundation
Flame

